Printing
The so-called printing is the processing process of making dye or paint into color paste, locally applying it to textiles and printing patterns. In order to complete textile printing, the processing method used is called printing process.
Pigment Printing
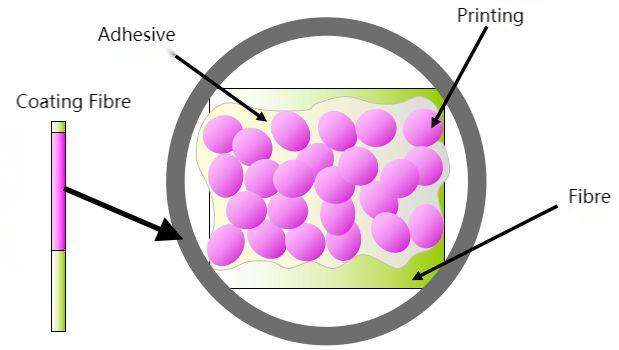
Pigment printing is a printing method in which the pigment is mechanically fixed on the fabric by means of high molecular polymer (adhesive) and water-insoluble colored substances (pigments) to form a firm, transparent and wear-resistant colored film on the fabric.
Dye printing
In terms of the mechanism of dye dyeing fiber, printing and dyeing are the same, except that in printing, the dye of a certain color is applied locally to the textile according to the requirements of the pattern, and after a certain treatment, the dye dyes the fiber, and then the printed products with one or more colors are obtained on the textile. Therefore, printing can also be said to be “local dyeing”.
Coloring principle of paint
Pigment printing is a printing method that stops the adhesive from forming a firm, transparent and wear-resistant film on the fabric, so as to mechanically fix the paint on the fabric.
Coloring materials of dyes
Dyeing is a processing process in which textile materials obtain bright and firm colors through the physical, chemical or physical-chemical combination of dyes (or pigments) and textile materials.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pigment Printing
Advantages:
• Simple use, simple process, high labor productivity, can reduce wastewater discharge
• Wide chromatogram, high lightfastness, clear printing lines and contours
• It is suitable for special printing methods, and can also be used for discharge and anti dyeing printing
• Easy color matching and good color light reproduction
• It is suitable for fabric printing of various fiber materials, especially blended fabrics.
Disadvantages:
• Poor hand feel, poor dry and wet rubbing fastness
• The use of kerosene in emulsified paste pollutes the air; Most of the monomers used to prepare adhesives are toxic
• The color brightness is not as bright as that of dye printing with equivalent structure
• The adhesive is easy to peel and block the mesh
Dye printing (taking reactive dyes as an example)
Advantages:
• There are many varieties, complete chromatograms and bright colors
• It is convenient to prepare color paste, simple printing process, good effect and few defects
• Good fastness to wet treatment
• Low printing cost and easy color matching
Disadvantages:
• Most of them are not resistant to chlorine, and the fixation rate is low. Some reactive dyes have great directness (affinity), which is easy to cause staining when soaping, especially when printing deep and thick colors.
Difference:
The biggest difference between dye printing and pigment printing is that pigment printing is combined with fabric by physical bonding, while dye printing is directly combined with fabric by van der Waals force.
Pigment printing can be used for the processing of any fiber textiles. It has more advantages in the printing of blends and interwoven fabrics. It has simple process, wide chromatography, clear flower shape outline, but poor hand feel and low rubbing fastness. Their light fastness and dry cleaning fastness are good, even excellent, so they are widely used in decorative fabrics, curtain fabrics and clothing fabrics that need dry cleaning.
How to distinguish between dye printing and pigment printing
Pigment printing and dye printing can be distinguished by comparing the hardness difference between the printed part and the unprinted part of the same fabric. The hand feel of the paint printed area is slightly harder than that of the unprinted area, which may be a little thicker. If the fabric is printed with dyes, there is no obvious hardness difference between the printed part and the unprinted part.
Post time: Jul-11-2022